Technical article
Technical article
[Bookmark] Automated Filling Solutions for Cell Banks, Strain Banks, and Plasmid Banks
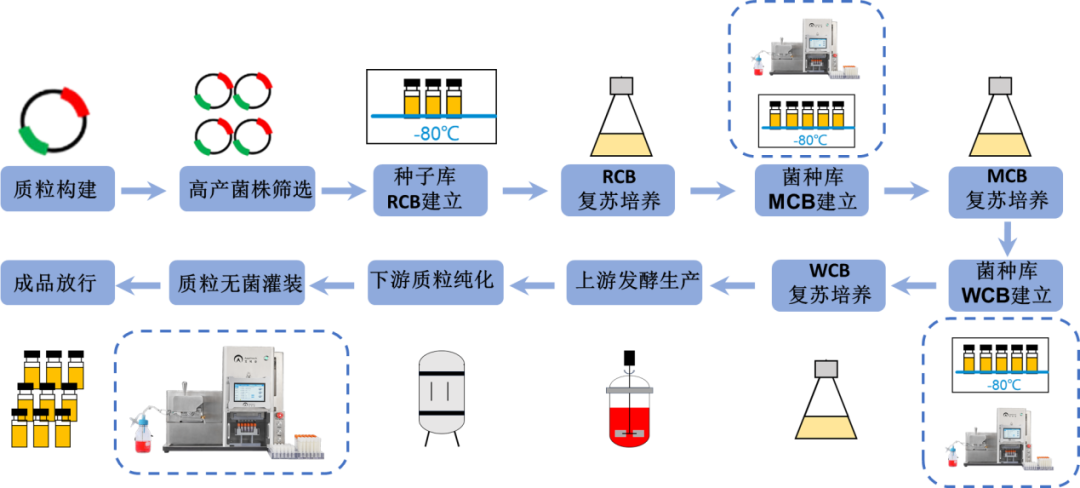
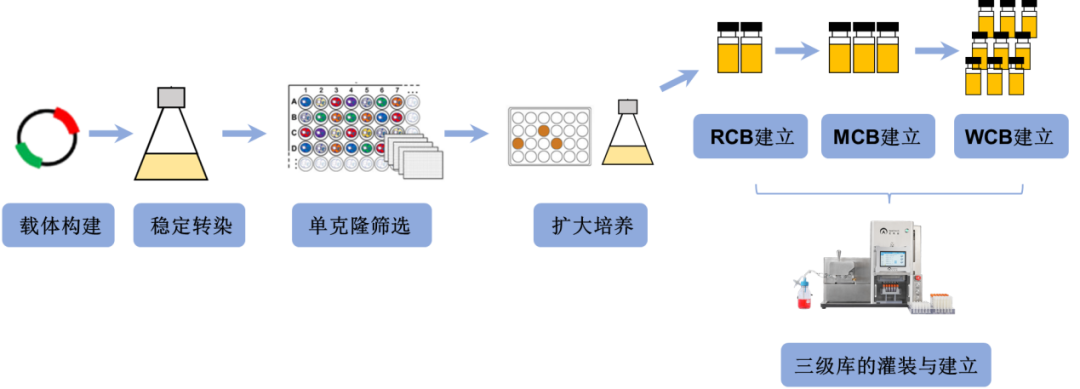
The development and production of any antibody drug start with the cell line. Establishing a cell bank is a crucial step in cell line management and must be prepared under the conditions that comply with China's current Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Currently, the world's most authoritative cell bank institutions or research institutes adopt a three-tier cell bank management system: the Primary Cell Bank (PCB), the Master Cell Bank (MCB), and the Working Cell Bank (WCB). In certain special cases, a two-tier management system of cell seed and master cell bank can be used, but it requires approval from the State Drug Administration.
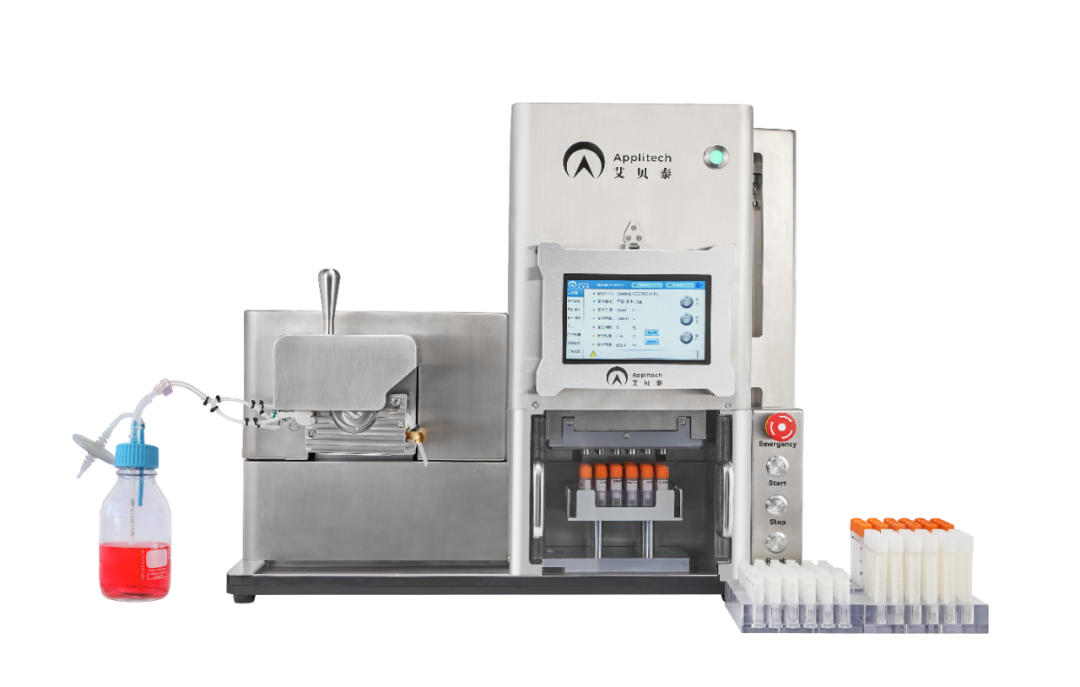
The establishment of a three-tier cell bank ensures the production of biological products with qualified, consistent quality cells that can be stably passaged. The AbioFill V100 filling equipment can easily achieve large-scale cell filling through automated operation.
Sharing How the AbioFill V100 Automates CHO Cell Filling from a User Perspective, Assisting in Cell Bank Establishment, and Evaluating Parameters such as Volume, Density, and Viability Compared to Manual Filling.
CHO Cell Filling Experiment
Experimental Materials:
- Cells: CHO Cells
- Cryopreservation Solution: Medium + DMSO
- Cryovials: Corning 430659 (2ml, External Thread)
- Equipment: Programmable Freezing Box, etc.
Instruments and Equipment:
- Filling System: AbioFill V100 Cell Filling System
Experimental Procedure:
Parameter Settings
- Filling Mode: Open-Cap - Fill - Close-Cap
- Filling Flow Rate: 350μL/s
- Filling Volume: 1000μL
Installation of Disposable Filling Tubes
- Use CPC quick connectors to connect the disposable filling tubes with the shake flask containing the sample to avoid contamination of cell samples during the operation.
Numbering and Installing Cryovials
- Number the cryovials to ensure sample representativeness for subsequent analysis. A total of 120 cryovials are filled, with samples from positions A1 and D6 from each plate selected for testing.
Filling Process
- Perform the filling using the AbioFill V100 system.
Results Analysis
In this experiment, manually filled cells were used as a control. Before filling, the cell samples were counted to determine their viability and density. After filling, samples from positions A1 and D6 of each plate (total of 10 samples) were selected for testing viability, density, and volume.
Viability and Density Testing:
- Purpose: To evaluate if the filling equipment causes any damage to the cell samples.
Volume Testing:
- Purpose: To assess the precision of the filling system.
Post-Filling Procedure:
- The filled samples were cryopreserved using conventional methods.
- One week later, the samples were thawed, and their viability and density were counted (data not shown).
- On the third day post-thaw, viability and density tests were conducted again, and the doubling time (DT) was calculated to evaluate if the equipment affects the cell growth.
Comparison Table: Manual vs. Automated Filling Method
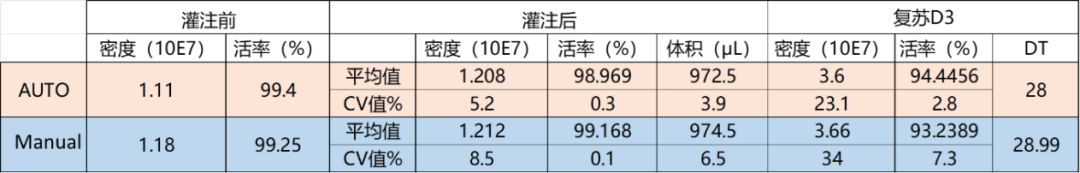
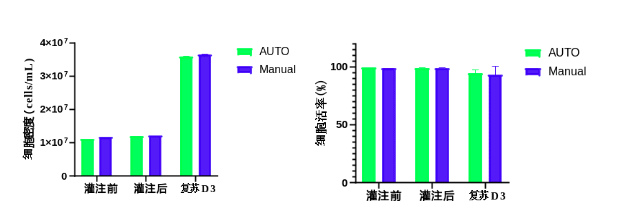
Manual vs. Automated Filling Method: Comparison of Cell Density and Viability Before and After Filling, and After Thawing on Day 3
Results Analysis
Comparison Before and After Filling:
Within Groups (AUTO and Manual):
- No significant differences were observed within each group before and after filling.
Between Groups (AUTO vs. Manual):
- The CV (Coefficient of Variation) for cell density and filling volume was lower in the AUTO group compared to the Manual group.
- The CV for cell viability showed a minimal difference between the two groups.
Post-Thaw Day 3 (D3):
- Between Groups (AUTO vs. Manual):
- The CV for cell density in the AUTO group was 10.9% lower than in the Manual group.
- The CV for cell viability in the AUTO group was 4.5% lower than in the Manual group.
- There was no significant difference in DT (Doubling Time) between the AUTO and Manual groups, indicating that the filling process did not cause any cell damage or alter cell proliferation patterns.
General Observations:
- There was no contamination during the filling process.
- Overall results were satisfactory.
- The AUTO filling method outperformed the manual method before and after filling, as well as after freezing and thawing.Other Applications of AbioFill V100